Describe Solids Liquids and Gases Using the Kinetic Theory
Kinetic Molecular theory Gases Describe how gases liquids and solids compare using the following table. As is discussed in Kinetic Theory an increase in temperature implies an increase in the kinetic energy of the individual atoms.
The Kinetic Theory Of Gases Kinetic Energy Of A Molecule
Solids Liquids and Gases.

. The energy required to change a substance from solid to liquid at its melting point. 32 The kinetic molecular theory ESAAL The kinetic theory of matter helps us to explain why matter exists in different phases ie. Solid The particles are arranged orderly and closely packed.
In this process a liquid converts into a gas. 2 Gases are relatively easy to compress while solids are virtually. We gain a better understanding of pressure and temperature from the kinetic theory of gases which assumes that atoms and molecules are in continuous random motion.
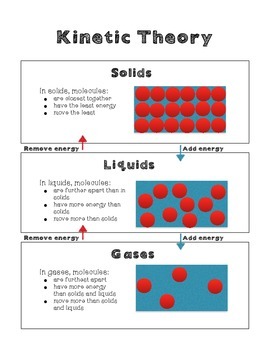
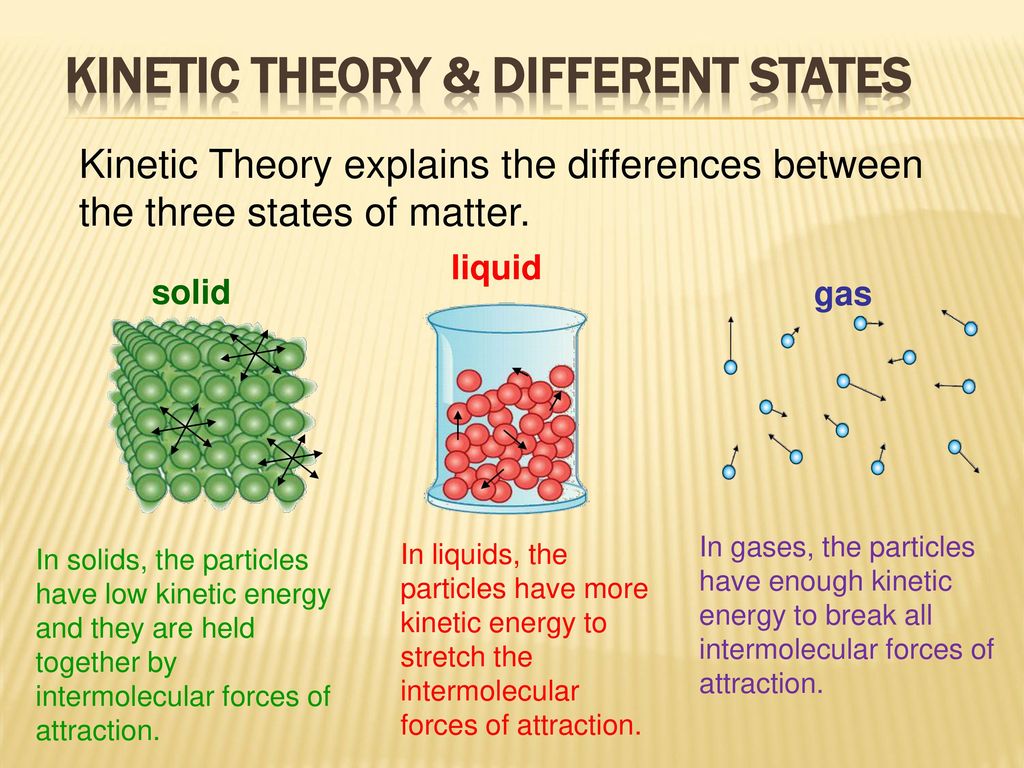
The attractive forces between them are very strong but their kinetic energy is very low. All matter is composed of small particles atoms molecules and ions. There is more than 1 version of this but in general the Molecular Kinetic Theory states that.
Liquid A state of matter which is characterized as. Solid liquid and gas and how matter can change from one phase to another. Kinetic theory Particles are in constant motion.
There are energy changes when changes in. Describe kinetic molecular theory. A force is thus exerted on the wall creating pressure.
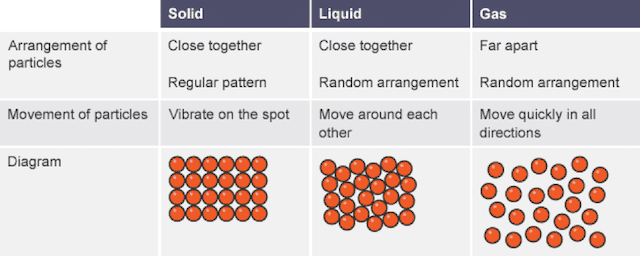
Thus they vibrate about fixed positions. KMT is most often referenced in relation to the behavior of. Solids Liquids Gases Volume definite or indefinite Molecular Motion high med low Distance Between Molecules g 2.
The gaps between the gas particles are larger than the particles themselves which is not observed in liquids and solids. Describe how gases liquids and solids compare using the following table. The Kinetic Theory of Matter describes the three different states of matter.
Solids Liquids Gases Volume definite or indefinite Molecular Motion high med low Distance Between Molecules 2. Use these concepts to explain the behaviour of materials undergoing heating in a variety of contexts. What is kinetic energy.
This is also why solids are difficult to compress. Solids Liquids and Gases Kinetic Theory The kinetic theory is an explanation of how particles in matter behave. The only influence gas particles have on.
Describe how gases liquids and solids compare using the following table. The kinetic theory of matter also helps us to. The force of attraction also is the reason why solids are close together.
View Kinetic-theory-gassesppt from MECHANICAL PHX-101 at National Institute of Technology Jalandhar. In your answer you should describe the. Describe kinetic molecular theory.
The Kinetic Theory of Matter states that all matter is composed. Identify each statement as True or False. C11-1-04 Explain the process of melting solidification sublimation and.
View the full answer. The three assumptions of the kinetic theory are as follows. Boiling point The temperature at which a liquid becomes a gas.
Kinetic Molecular Theory Name Period Unit 7 HW 1 Worksheet Goals 1 2 1. Random motion intermolecular forces elastic collisions average kinetic energy temperature C11-1-03 Explain the properties of liquids and solids using the Kinetic Molecular Theory. Kinetic theory the behaviour of gases Learning outcomes use.
SolidiquidsGates Volume definite or indefinite Molecular Motion high med low Distance Between Molecules Locslittle none 2 What is kinetic energy. Kinetic particle theory and state changes The kinetic particle theory explains the properties of solids liquids and gases. C11-1-02 Use the Kinetic Molecular Theory to explain properties of gases.
Now explain how the particles are arranged in a solid a liquid and gas using words. Draw clear diagrams that accurately describe how the particles are arranged in a solid a liquid and a gas. Solid The particles are arranged orderly and closely packed.
What is kinetic energy. 1 Solids have a definite shape and volume because solids shows that the force of attraction between the entities in the solid are very strong. Expert Answer 100 3 ratings Questions 1 The Kinetic Theory of Matter describes the three different states of matter.
Watch this clip which explains about the particle arrangements in a solid a. When a molecule collides with a rigid wall the component of its momentum perpendicular to the wall is reversed. Expert Answer Transcribed image text.
The attractive forces between them are very strong but their kinetic energy is very low. In a solid unlike in a gas the atoms or molecules are closely packed together but their kinetic energy in the form of small rapid vibrations pushes neighboring atoms or molecules apart from each other. These particles are in constant random motion.
Vaporization The process where the particles that make up a liquid move fast enough to escape the attractive forces of the other particles. Kinetic Molecular Theory Definition KMT Kinetic Molecular Theory KMT describes the experimentally discovered behavior of particles. In a solid they may just vibrate next to each other but in a liquid or gas they travel much faster.
Objectives Be able to describe the differences between the arrangement of the particles in solids liquids and gases. According to the basic assumption.
Kinetic Theory Solids Liquids Gases By True North Tpt

Solids Liquids Gases And Plasmas Ck 12 Foundation

Gases Liquids Solids States Of Matter Kinetic Particle Theory Models Diagrams State Changes Melting Boiling Evaporation Condensing Freezing Solidifying Cooling Curves Particles Pictures Elements Compounds Mixtures Heat Conduction Electrical
Comments
Post a Comment